
A User is generally a person who operates or conrtrols a computer or network service. A user has a user account which the network system usually identified by a user name.Since users has access to the system, they can do anything that they're allowed to at their will. People using a computer should have a account to access it next time. 3 important attributes are: Commerce, Entertainment and Information.

A Browser is used to browse and interact information throughout the World Wide Web. Information is identified by a URL(Uniform Resource Location) which is basicially a site. Known browsers are: Google, Yahoo and Bing.

A Device is a piece of mechanical equipment that is used by users. Devices are always used everyday for various reasons like: Web Browsing,social media and entertainment. A common device is a PC, which everyone should own. In order to use the device, a user is required to use it, no matter how good the device is it's pretty much useless without a user. In order for a device to connect to the internet, the Internet Service Providers will need to grant the user's device access to connect. Another popular device is phones, which allows you to make phone calls.
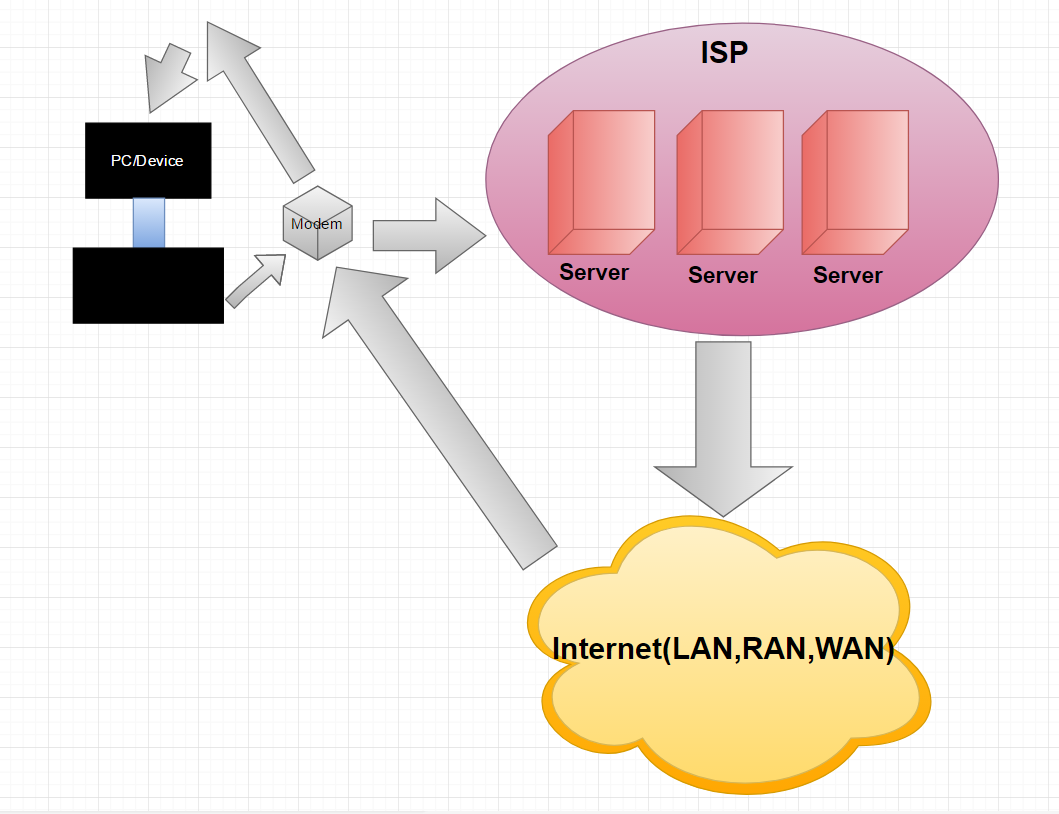
A Internet Service Provider is a company that provides server accessing for users to the internet. Internet Service Provider companies may make it for a purpose whether it's public, or for commerical advertisments or privately owned, every provider does the same thing. If you were to connect with someone in your area, the local area network (LAN) provider will connect with the person you're trying to communicate with.

A Webpage is a document that is suitable for the World Wide Web and web browsers. Webpages are ususally written in HTML, or any other markup language simillar to HTML.Most webpages contain hypertext that incudes a navigation bar or a sidebar full of contents that may take you to other webpages, hence the hyperlink, we mainly refer them as links.

TheWorld Wide Web is a global information system which allows all of the hypertext documents connected together. Also abbreviated as WWW, this system stores all of the Webpages. Users can search for any webpage,document or URL on the World Wide Web to recieve info from the specified link they want.
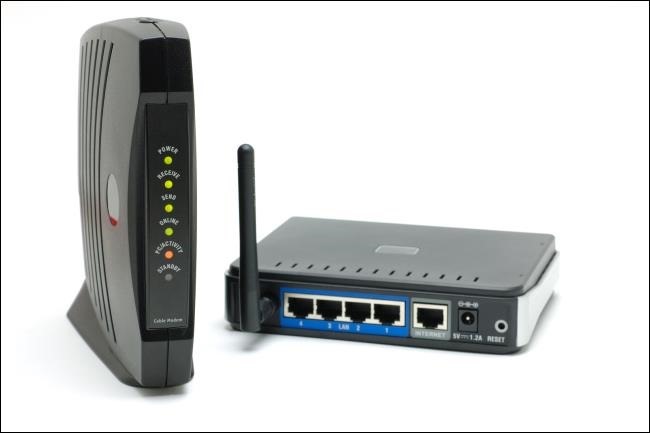

A Modem is a network hardware that modulates one or more signal waves to decode information for transmission and demodulates signals to decode the transmitted information. Modems are generally classified by the maximum amount of data they can send in a given time, which is identified as bits per second. The modem can also measure audio waves per second, by a method called baud.

The Network is basically one of the major systems of the internet created to do anything in our everyday lives. The network can share resources,data and travel them around all around the network system to different users. A network that can create, send and terminate data are called network nodes. Nodes can include hosts such as personal computers, phones, servers as well as networking hardware. Networks cansupport an enormous number of applications and services such as access to the World Wide Web.
A Webserver is where all the webpages are stored in one, huge server. They all connect together, which is accessed by the world wide web. A webserver uses HTTP(Hypertext transfer protocol) to proccess request coming from the users. All webservers provide services to other computers as well.

A Fiber Optic Cable is a thread of glass made to reflect light. When you send a beam of light down a cable, light bounces up and down the cable until it is received at the other end. Depending on the bounce angle, you can actually send multiple bits at the same time, with all of them travelling at the speed of light. Fiber Optic Cables have been replaced with copper wires because light travels faster than copper, with the fastest copper wire roughly up to 1GB per sec.
Webhosting is when a computer runs a alot of websites at the same time with the same address or domain name. Ususally any website from small to large may only require one webhoster to function properly. Other users can webhost a server so they can make their webpage/web address accessiable to the World Wide Web. This allows other users to view it.
Packets are small bits of information of data sent from one place to another. This is controlled by routers and TCP which is: Transmission Control Protocol. Both of these Protocols monitors the packets moving from routes to it's address destination. Basicially the TCP checks whether the packets have been successfully recieved and acknowledged. If a packet went missing, the reciever will notify TCP that it hasn't been recieved. TCP then resends the missing packet. This procedure keeps repeating until all the packets are sent correctly and recieved. The destination and your device will notify each other that all the packets are there.
Routers are a system or computer that sends bits of data down a copper or fibre optic cable and can reassemble whenever they reach their destination or when they need to. They also create various paths that they can travel accross, even if one of the routes ain't working. Routers are reliable when it comes to sending or recieving info from.
URL, also known as "Uniform Resource Location", is the address of a world wide web page. A URL can be anything like a site etc. A common URL has three main things: A protocol, a hostname and a file name. An example of a URL looks like this: https://neocities.org
If you want to visit this website next time, feel free to click on and save the link below :)

Here are also some Khan Academy computing videos to get to know more about how the internet works!
